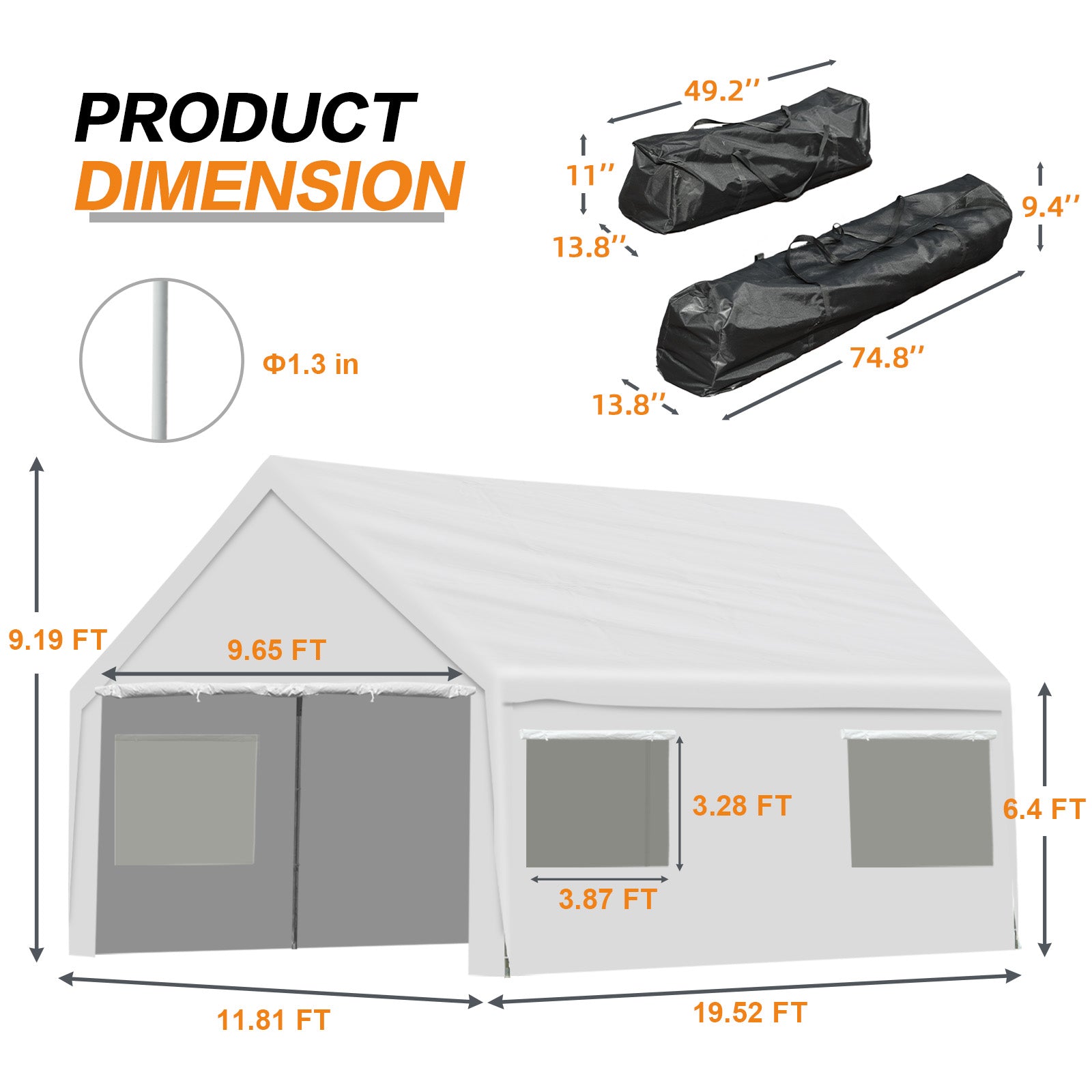
Introduction
Considering a greenhouse but unsure about the various types and styles available for your backyard? At Aoodor Shop, we specialize in helping American gardeners select the right greenhouse solutions that transform ordinary backyards into thriving growing spaces. This comprehensive guide explores the various types and styles of greenhouses available today, with a particular focus on compact options, including mini outdoor greenhouses and small greenhouses, ideal for your garden. We'll cover everything from basic greenhouse fundamentals to specific styles, materials, and the perfect compact solutions for home gardening success.
What Are Greenhouses? Understanding the Basics
Definition and Purpose of Greenhouses
A greenhouse is a controlled environment structure designed to extend growing seasons, protect plants from harsh weather, and create optimal conditions for plant growth. These transparent or translucent structures harness solar energy while protecting from wind, rain, snow, and temperature extremes.
The primary purposes of greenhouses include:
|
Purpose |
Benefit |
|
Season Extension |
Grow plants year-round regardless of outdoor climate |
|
Plant Protection |
Shield delicate plants from weather and pests |
|
Controlled Environment |
Manage temperature, humidity, and light exposure |
|
Early Plant Starting |
Begin seedlings before outdoor growing season |
Importance of Structure and Material in Greenhouse Selection
The effectiveness of any greenhouse depends heavily on its structural design and material composition. Frame strength determines durability and weather resistance, while covering materials affect light transmission, insulation properties, and maintenance requirements.
When selecting from the various types of greenhouses available, consider how structure and materials align with your climate, intended use, and budget. Quality construction ensures your greenhouse investment provides years of reliable growing space.
Types of Greenhouses: Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the different styles of greenhouses helps you choose the perfect option for your specific gardening needs and space constraints.

Lean-to Greenhouses: Space-saving Design Attached to a Building
Lean-to greenhouses attach directly to existing structures, making efficient use of limited space while providing convenient access.
Special Features:
- Shared wall reduces construction and heating costs
- Easy access to utilities and electricity
- Perfect for small yards and urban spaces
- Enhanced structural stability

Freestanding Greenhouses: Standalone Structures Offering Maximum Growing Space
Independent structures that can be positioned for optimal sun exposure and scaled to match your growing needs.
Special Features:
- 360-degree light exposure
- Complete design and size flexibility
- Superior air circulation
- Can accommodate larger growing operations

Hoop/Quonset Greenhouses: Dome-shaped, Cost-effective, Easy to Assemble
Curved, tunnel-like design that's economical and functional with excellent strength-to-weight ratios.
Special Features:
- Semi-circular design for wind resistance
- DIY-friendly assembly process
- Cost-effective for large growing areas
- Typically uses plastic film covering

Gothic Arch Greenhouses: Arched Design Ideal for Snow and Rain Runoff
Pointed arch design that efficiently sheds weather while maximizing interior space and headroom.
Special Features:
- Superior snow and rain shedding
- Increased headroom over standard arches
- Attractive architectural appearance
- Excellent structural strength

A-Frame and Modified A-Frame: Traditional Shapes with Efficient Illumination
Triangular profiles that provide good light penetration and straightforward construction methods.
Special Features:
- Simple, sturdy triangular construction
- Efficient light distribution throughout
- Cost-effective material usage
- Suitable for moderate climate zones

Ridge and Furrow Greenhouses: Large, Connected Structures for Commercial Growing
Connected greenhouse units with shared sidewalls, creating expansive growing areas with efficient climate control.
Special Features:
- Shared walls reduce per-square-foot costs
- Centralized heating and cooling systems
- Streamlined crop management workflows
- Easily scalable for expansion
Specialty Greenhouses: Hydroponic, Cold-frame, Educational, and Research Greenhouses
Special Features:
- Hydroponic: Soilless growing system integration
- Cold-frame: Low-profile season extension design
- Educational: Demonstration and learning focused layout
- Research: Precision climate and environmental controls
Styles of Greenhouses by Material
The materials used in greenhouse construction significantly impact performance, durability, and long-term costs. Understanding the characteristics of different frame and covering materials helps you make informed decisions that align with your specific needs and budget.
Frame Materials
Wood Frames
Wood frames offer natural beauty and excellent insulation properties, with cedar, redwood, and pressure-treated lumber being the most popular choices. They provide superior thermal performance and help maintain stable greenhouse temperatures, particularly valuable in colder climates. However, wooden frames require regular maintenance including staining or sealing every few years to prevent rot and insect damage.
Aluminum Frames
Aluminum frames are the most popular choice for modern greenhouses due to their exceptional durability and minimal maintenance requirements. These lightweight yet strong frames resist corrosion and deterioration while allowing for larger glass panels and more open interior space. While aluminum provides poor insulation compared to wood, its longevity and low maintenance make it cost-effective over time.
PVC Frames
PVC frames offer an economical entry point into greenhouse gardening, particularly suitable for temporary or seasonal structures. These lightweight frames are easy to work with and provide better insulation than aluminum while resisting moisture effectively. However, UV radiation can degrade PVC over time, making them best suited for smaller greenhouse designs where replacement costs remain reasonable.
Steel Frames
Galvanized steel frames provide maximum strength and durability for large or commercial greenhouse applications. They can support substantial loads and withstand extreme weather conditions better than other materials, making them ideal for permanent installations. Proper galvanizing protects against rust for decades, though the higher cost limits their use to heavy-duty applications.
Covering Materials
Glass Covering
Glass remains the premium choice for greenhouse coverings, offering maximum light transmission and traditional aesthetic appeal. High-quality greenhouse glass allows up to 90% light transmission while providing excellent clarity and complete recyclability. The main drawbacks include higher cost, weight requirements, and vulnerability to hail or impact damage.
Polycarbonate Panels
Polycarbonate panels combine excellent insulation, durability, and light transmission in a lightweight package. Twin-wall designs provide superior insulation compared to glass while offering excellent impact resistance against hail and damage. UV-resistant coatings ensure long-term clarity and prevent degradation, making them increasingly popular for modern greenhouses.
Polyethylene Film
Polyethylene film offers the most economical covering option, making greenhouse gardening accessible to budget-conscious growers. The material is easy to install and replace, perfect for seasonal use or temporary structures. However, it degrades under UV exposure and requires replacement every 3-4 years, though the low cost makes this acceptable for many applications.
Acrylic Covering
Acrylic panels provide a lightweight alternative to glass while maintaining excellent optical clarity and weather resistance. The material offers good insulation properties and UV resistance without yellowing over time. While more expensive than plastic film, acrylic provides better longevity and maintains appearance better than most alternatives.
Material Comparison Overview
|
Material |
Durability |
Cost |
Maintenance |
Insulation |
Weather Resistance |
Best For |
|
Wood Frame |
Moderate (10-15 years) |
Medium |
High (staining/sealing) |
Excellent |
Good with treatment |
Traditional aesthetics, DIY builders |
|
Aluminum Frame |
Excellent (20+ years) |
Medium-High |
Very Low |
Poor |
Excellent |
Low-maintenance, modern design |
|
PVC Frame |
Good (8-12 years) |
Low |
Low |
Good |
Fair |
Budget-conscious, temporary structures |
|
Steel Frame |
Excellent (25+ years) |
High |
Medium (rust prevention) |
Poor |
Excellent |
Heavy-duty, commercial applications |
|
Glass Covering |
Excellent (20+ years) |
High |
Medium |
Good |
Fragile to hail |
Premium appearance, maximum light |
|
Polycarbonate |
Very Good (15-20 years) |
Medium-High |
Low |
Excellent |
Very Good |
Energy efficiency, impact resistance |
|
Polyethylene Film |
Fair (3-4 years) |
Very Low |
High (replacement) |
Fair |
Good |
Budget option, seasonal use |
|
Acrylic Covering |
Good (10-15 years) |
High |
Medium |
Good |
Good |
Lightweight glass alternative |
Small and Mini Outdoor Greenhouses: Perfect for Home Gardens
Definition and Benefits of Mini Greenhouses
Mini outdoor greenhouses, typically ranging from 4x4 feet to 8x12 feet, provide all the benefits of larger structures in compact, manageable sizes. These smaller greenhouses are perfect for homeowners who want to extend their growing seasons without dedicating extensive yard space.
Key Benefits:
- Space Efficiency: Fit in small yards, patios, or balconies
- Budget-Friendly: Lower initial investment and operating costs
- Manageable Maintenance: Easy to clean, organize, and maintain
- Versatile Placement: Flexible positioning for optimal conditions

Popular Models and Styles Suited for Balconies, Patios, and Small Yards
Small greenhouses come in various configurations designed for different spaces:
Tabletop Mini Greenhouses: Perfect for apartments and small patios, these compact units provide protected space for starting seedlings and growing herbs.
Lean-to Mini Greenhouses: Attach to existing structures, maximizing space efficiency while providing convenient access.
Portable Greenhouses: Lightweight, moveable structures that can be repositioned based on seasonal needs and sun patterns.
Vertical Tower Greenhouses: Maximize growing space in minimal footprints through vertical design.
Best Uses: Starting Seedlings, Growing Herbs, Winter Protection
Small greenhouses excel at specific gardening tasks:
|
Use Case |
Benefits |
Best Plants |
|
Seed Starting |
Controlled germination environment |
Tomatoes, peppers, flowers |
|
Herb Growing |
Year-round fresh herbs |
Basil, parsley, cilantro |
|
Winter Protection |
Shelter tender plants |
Geraniums, citrus, tropicals |
|
Succession Planting |
Continuous harvest cycles |
Lettuce, spinach, microgreens |
Explore our complete selection of greenhouse solutions and garden supplies to find the perfect growing environment for your needs.
FAQ
1. How to build a small greenhouse?
Building a small greenhouse involves selecting an appropriate location with good sun exposure, preparing a level foundation, assembling the frame structure, and installing covering materials. Start with a simple kit design for your first project, ensuring proper ventilation and door placement. Most small greenhouse kits include detailed instructions and can be assembled in a weekend with basic tools.
2. How to heat a small greenhouse?
Small greenhouses can be heated using electric heaters, propane heaters, or passive solar techniques. Electric heaters with thermostats provide reliable temperature control, while thermal mass materials like water barrels store and release heat naturally. Insulation techniques, such as bubble wrap on walls, help retain heat and reduce energy costs during winter months.
3. What to grow in a small greenhouse for beginners?
Beginners should start with easy-to-grow plants like lettuce, spinach, herbs, and radishes. These crops tolerate temperature fluctuations and provide quick harvests. Tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers are excellent next steps once you gain experience. Focus on plants that benefit from extended growing seasons or protection from weather extremes.
4. How to keep a small greenhouse warm in the winter?
Winter warmth strategies include using thermal mass objects, installing insulation materials, sealing air leaks, and adding supplemental heat sources when needed. Position water containers inside to absorb day heat and release it at night. Consider using row covers inside the greenhouse for additional plant protection during extremely cold periods.
Conclusion
Selecting the Right Greenhouse Type:
- Assess your space: Choose lean-to for small areas, freestanding for maximum flexibility
- Consider your budget: Hoop houses offer economy, while glass structures provide premium performance
- Match materials to climate: Polycarbonate for insulation, polyethylene for budget-conscious choices
- Start small if uncertain: Mini greenhouses provide excellent introduction to controlled growing
Professional Guidance Ensures Success: When exploring the various types of greenhouses available, professional consultation helps match your specific needs with optimal solutions. Consider factors like local climate, intended crops, available space, and long-term growing goals.
Combine Multiple Verification Methods: Before making your final greenhouse selection, research local building codes, evaluate your site conditions, and consider seasonal growing requirements. The right greenhouse type transforms your gardening experience and extends your growing capabilities throughout the year.
Ready to Transform Your Garden? Browse our premium greenhouse collection and discover the perfect type and style for your backyard growing dreams. Visit Aoodor Shop today!